Africa’s agriculture is undergoing a massive digital shift. Technology is no longer a luxury it’s the engine driving productivity, sustainability, and profitability. According to the World Bank, Agri-Tech could increase Africa’s agricultural productivity by up to 70% by 2030. From drones to AI-driven analytics, farmers and agribusinesses are using data to make smarter decisions, reduce waste, and boost yields.
Here are the Top 10 Agri-Tech trends shaping the future of agriculture across Africa.
Contents
- 1 1. Precision Agriculture and Smart Farming
- 2 2. AI and Machine Learning in Farming
- 3 3. Drone Technology for Crop Monitoring
- 4 5. Mobile Apps and Digital Marketplaces
- 5 6. Digital Financial Solutions and Agri-Fintech
- 6 7. Climate-Smart Agriculture Technologies
- 7 8. Agri-Digital Extension and e-Learning
- 8 9. Post-Harvest and Cold Chain Innovations
- 9 10. Data-Driven Policy and Research Platforms
- 10 Did You Know?
- 11 FAQ
- 12 Conclusion: The Future of Agriculture Is Digital
1. Precision Agriculture and Smart Farming
Precision farming uses data, sensors, and analytics to optimize every input :water, fertilizer, seeds, and time.
- Tech Tools: GPS mapping, drones, IoT soil sensors.
- Impact: Farmers save up to 25% on inputs and increase yield by 20–30%.
- Example: In Kenya, startups like Illuminum Greenhouses use IoT to monitor temperature, humidity, and soil health remotely.


2. AI and Machine Learning in Farming
Artificial intelligence is enabling farmers to predict weather, diagnose crop diseases, and make informed planting decisions.
- Impact: AI tools can reduce crop losses by up to 40% through early detection of pests and diseases.
- Example: Hello Tractor’s AI platform connects tractor owners with farmers, optimizing machinery use across regions.
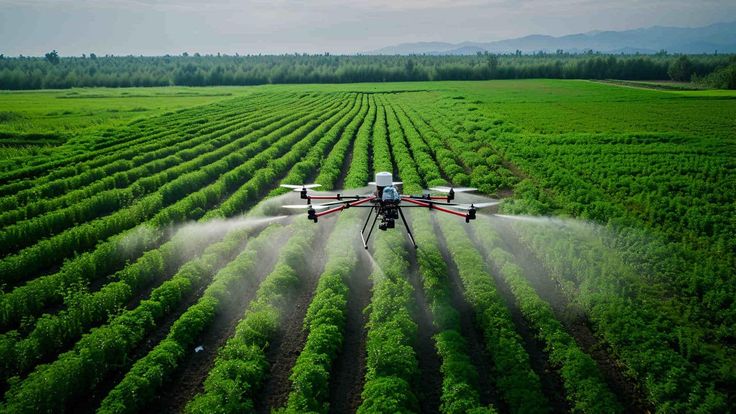
3. Drone Technology for Crop Monitoring
Drones are becoming an essential part of modern farming. They help with aerial mapping, spraying, and plant health monitoring.
- Impact: Drones increase spraying efficiency by up to 90% and cut labor costs.
- Example: In Nigeria, AirSmat uses drones and AI to provide real-time farm intelligence


5. Mobile Apps and Digital Marketplaces
Mobile AgriTech platforms are closing the gap between farmers, buyers, and input suppliers.
- Impact: Apps provide farmers access to markets, finance, and weather alerts—improving income stability.
- Example: Twiga Foods (Kenya) links smallholders to urban markets, reducing post-harvest losses by 30%.
6. Digital Financial Solutions and Agri-Fintech
Access to finance remains a major bottleneck in African farming. Agri-Fintech solutions are changing that through mobile loans, insurance, and credit scoring.
- Impact: Over 200 million African farmers now use mobile money platforms for financial inclusion.
- Example: Apollo Agriculture (Kenya) uses satellite data and machine learning to offer input credit and insurance to smallholders.
7. Climate-Smart Agriculture Technologies
With increasing droughts and floods, climate-smart tools like solar irrigation and drought-tolerant seeds are crucial.
- Impact: Solar irrigation can cut water waste by 30% and energy costs by 40%.
- Example: The SoLAR Phase II Project in East Africa is scaling solar-powered irrigation to boost resilience.


8. Agri-Digital Extension and e-Learning
Farmers are now learning through digital platforms instead of traditional extension visits.
- Impact: E-extension reduces the cost of knowledge delivery by up to 60%.
- Example: eSoko and Digital Green offer SMS-based advisory services on crop management and market trends.
9. Post-Harvest and Cold Chain Innovations
Up to 40% of Africa’s food is lost post-harvest due to poor storage and logistics.
- Tech Innovations: Solar-powered cold rooms, smart packaging, and mobile logistics apps.
- Example: ColdHubs (Nigeria) provides pay-as-you-go solar cold storage to reduce food spoil
Read more onPost Harvest Losses in Africa: Challenges, Solutions & the Future of Food Security
10. Data-Driven Policy and Research Platforms
Governments and organizations are embracing data-driven agriculture to inform policies and investments.
- Impact: Better data supports smarter subsidies, risk mapping, and resource allocation.
- Example: The SAGDA platform (Synthetic Agriculture Data for Africa) provides open-source data for AI and policy use.
Did You Know?
- Africa’s AgriTech market is projected to reach $1 trillion by 2030.
- Only 4–6% of Africa’s farmland is irrigated, compared to 37% in Asia, signaling huge potential for tech-driven irrigation.
- Over 400 AgriTech startups now operate across the continent, with Kenya, Nigeria, and South Africa leading.
FAQ
Q1: What is AgriTech in simple terms?
AgriTech refers to the use of technology—AI, IoT, drones, and digital platforms—to make agriculture more efficient and profitable.
Q2: Why is AgriTech important in Africa?
It helps address low productivity, food insecurity, and climate change by providing real-time solutions and data-driven decision-making.
Q3: How can agribusinesses start adopting AgriTech?
Start small: integrate mobile data systems, digital finance tools, or IoT-based monitoring depending on business needs.
Conclusion: The Future of Agriculture Is Digital
AgriTech is no longer the future it’s the present and the path forward. With the right policies, investments, and training, Africa can feed its people, strengthen exports, and grow sustainable economies.
Institutes like IRES play a key role in this transformation building the digital and technical skills professionals need to lead Africa’s AgriTech revolution.
I am a passionate digital marketing and communication professional with a strong background in content creation, social media management, graphic design, and campaign strategy. Over the years, I’ve gained hands-on experience developing digital content, managing brand presence across platforms, and driving engagement through storytelling and data-informed decisions. My work is guided by creativity, purpose, and a deep commitment to helping brands connect meaningfully with their audiences. You can reach me at [email protected] for inquiries.








Comment here